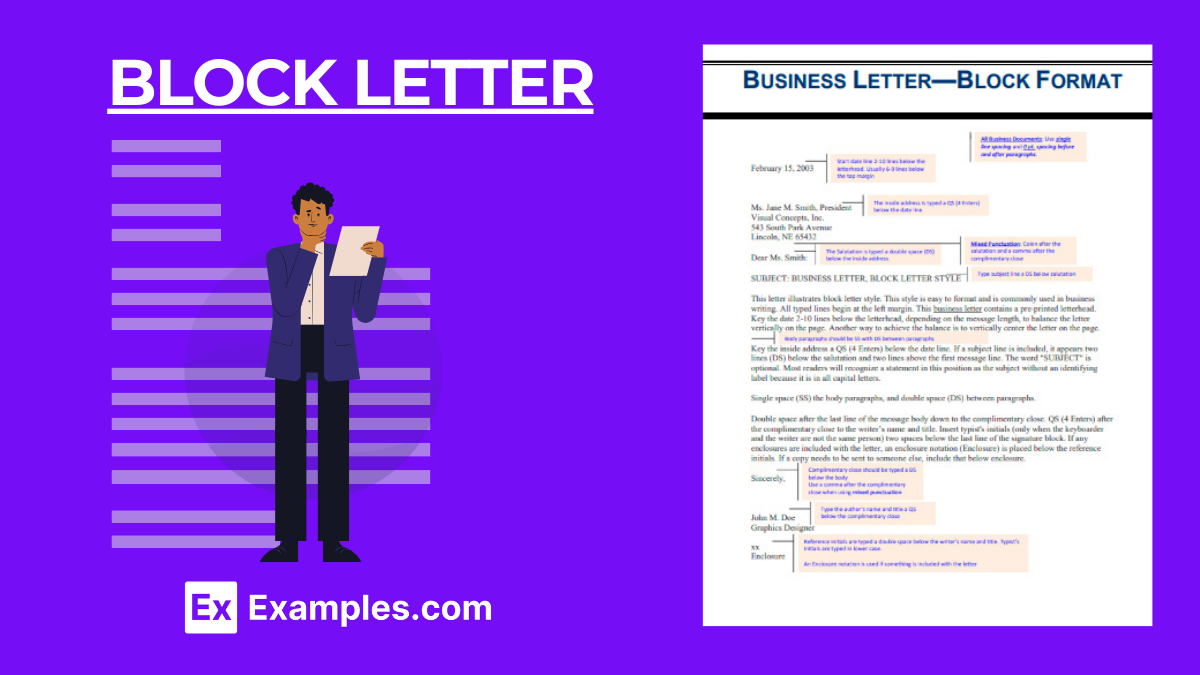

Whether you’re applying for a job, sending a business letter, or writing a cover letter, the way you present your message is just as important as the message itself. That’s why it’s crucial to pay attention to the format of your writing. One popular format that can help you achieve a professional and polished look is Block Letter Format.
A block letter refers to a style of writing or formatting used in formal business correspondence. In this format, all text is aligned to the left margin, creating a “block” of text that’s easy to read. Block letter format typically includes single-spaced lines with a double space between paragraphs, and it does not indent paragraphs. This style is widely used because it presents a neat, organized appearance, making it a standard for professional communications. It includes elements such as the sender’s address, date, recipient’s address, salutation, body of the letter, closing, and the sender’s signature
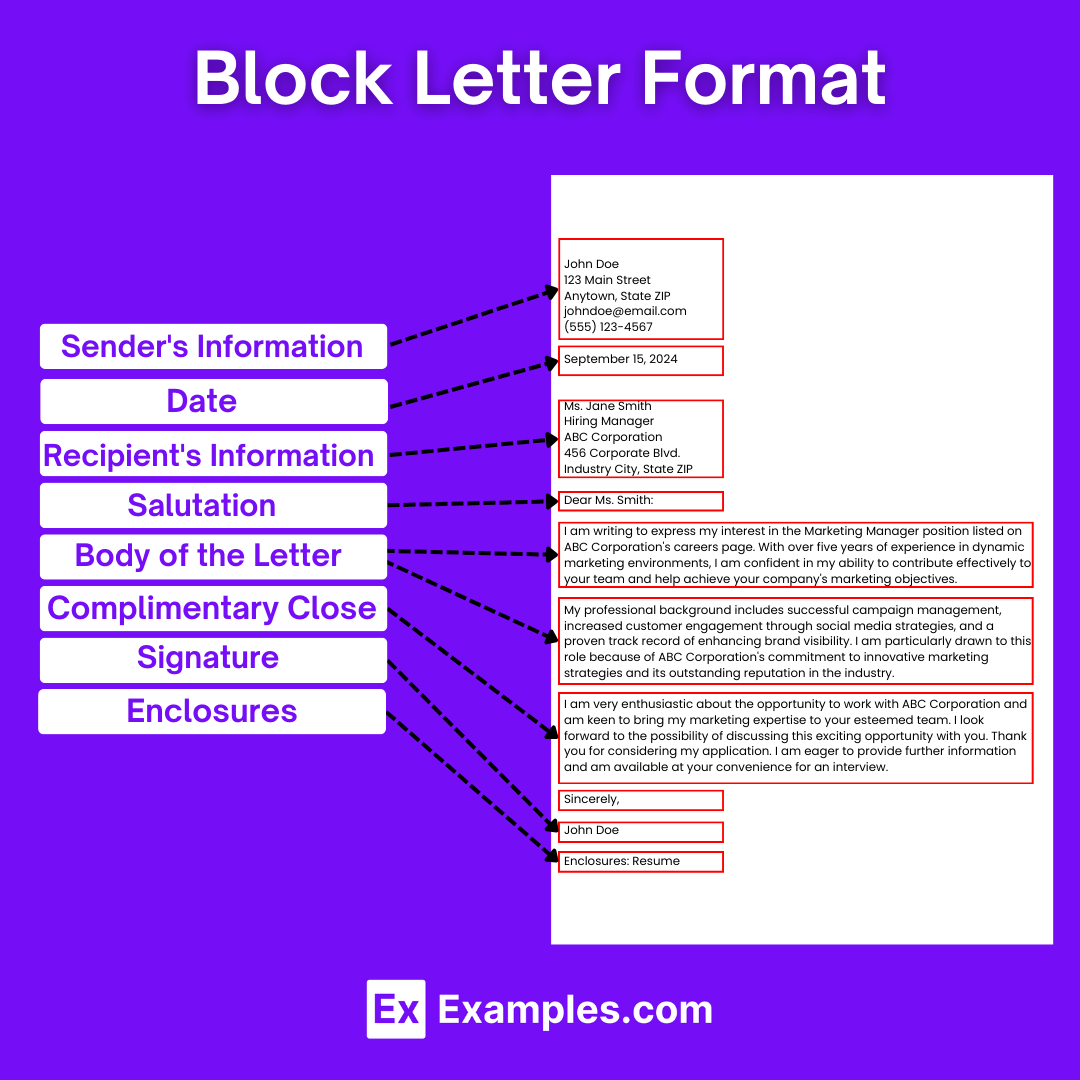
[Your Address]
[City, State, Zip Code]
[Email Address]
[Phone Number]
[Date][Recipient’s Name]
[Recipient’s Title]
[Company’s Name]
[Company’s Address]
[City, State, Zip Code]Dear [Recipient’s Name]:
[Body of the Letter]
Sincerely,
[Your Signature (if sending a hard copy)]
[Your Typed Name]Enclosure(s): [List of enclosed documents, if any]
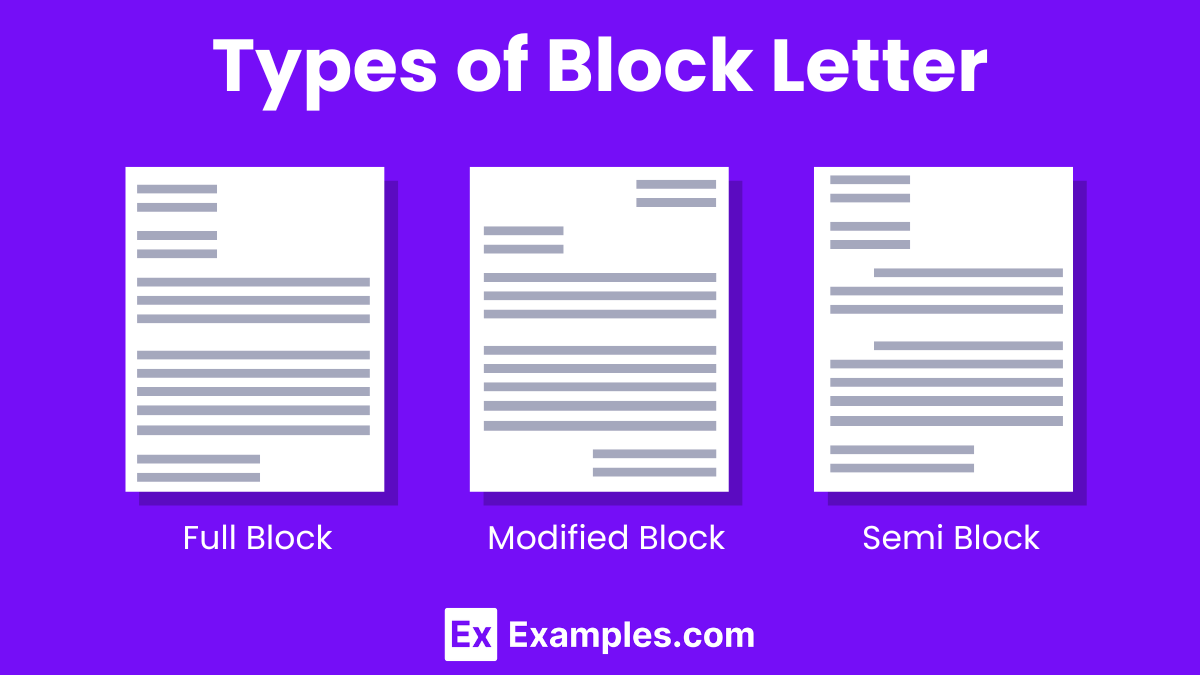
The Full Block Style is the most formal and commonly used format in business and official correspondence. In this layout, every element of the letter, including the sender’s address, date, recipient’s address, salutation, body, closing, and signature, aligns to the left margin. There are no indented lines, creating a uniform and clean appearance. This style emphasizes professionalism and simplicity, making it a popular choice for formal communications.
The Modified Block Style offers a blend of formality and modern design. It distinguishes itself from the full block style by positioning the sender’s address, date, complimentary close, and signature towards the center or right side of the page, while the rest of the content aligns to the left. This style maintains a professional look while introducing an element of visual interest, making it suitable for business letters that seek a balance between tradition and contemporary aesthetics.
The Semi-Block Style, also known as the Indented Style, combines elements of the full block and modified block styles with a traditional twist. While it aligns the sender’s address, date, and closing to the right, similar to the modified block style, each paragraph in the letter’s body starts with an indentation. This format adds a degree of formality and structure to the document, making it appropriate for business letters that require a more traditional approach while still adhering to professional standards.
Effective communication is a key aspect of professional relationships, whether in the workplace or beyond. By following these simple steps, you can create a professional and effective letter using the Block Letter Format.
This section delves into the nuances distinguishing formal letter from block letters, emphasizing their respective uses, structural differences, and formatting norms. Through a detailed comparative table, we aim to provide a clear understanding of how formal letters vary from the block letter format, catering to different communication needs.
| Feature | Formal Letter | Block Letter |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A type of letter used for official or serious occasions. | A style of writing or formatting letters, often used in formal contexts. |
| Purpose | To convey official requests, complaints, or to provide information. | To ensure clarity and legibility, regardless of the letter’s content. |
| Formatting | May follow various formats including block, modified block, etc. | Characterized by a specific alignment; all text is justified to the left margin. |
| Tone | Usually formal and professional. | Can be formal or informal, depending on the context of the letter. |
| Usage | Used in business, academic, and other formal settings. | Used in both formal and informal settings; preferred for its readability. |
| Examples | Business proposals, academic applications, official complaints. | Business letters, personal letters, educational materials. |
| Distinct Features | Formal language, specific conventions like salutation and closing. | Uniform lettering style and spacing, often employing a full block format. |